Languages
Wet Limestone

Advantages
- High removal efficiency
- Low sorbent and power consumption
- High reliability and availability
- Stable byproduct (commercial grade gypsum)
Projects
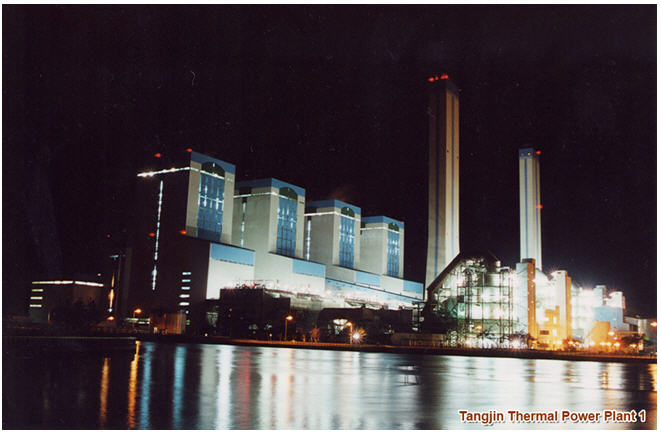
- Dangjin Thermal Power Plant Units 1~4
500MWX 4, Korea (1995)
- Cheongju Local Heating Public Cooperation, Korea (2000)
- Samcheonpo Thermal Power Plant Units 1~4
560MW X 4, Korea (2002)
- Hadong Thermal Power Plant Units 7~8
500MW X 4, Korea (2006)
Wet Limestone- Gypsum Process
Sulfur oxide (SOx) emitted during the burning of fuel is highly toxic and causes acid rain. It is generated by facilities that burn fuel containing sulfur, such as coal and oil.
The wet limestone-gypsum process uses a wet scrubber to remove SOx from flue gas. Limestone or slaked lime is used as sorbent. As the sorbent reacts with SOx, gypsum is generated as a byproduct. The discharged gypsum is recycled to make gypsum board or cement.
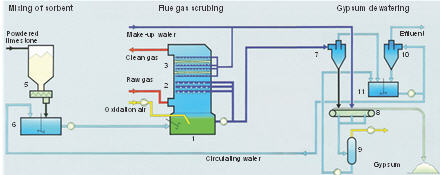
SO2 is removed from flue gas in the absorber or scrubber tower using limestone slurry.
The absorbed SO2 is oxidized in the absorber sump to form marketable calcium sulfate crystals (gypsum). The pH level in the absorber sump, which changes depending on the quantity of SO2 removed in the absorber, is controlled by adding limestone slurry. This enables continuous production of high purity gypsum.
Gypsum slurry from the absorber sump is thickened in a hydrocyclone and then more than 90% is dewatered by a vacuum belt filter. Alternatively, a centrifuge may be used in place of the vacuum belt filter.
|
1. Absorber sump 2. Absorption zone 3. Demister 4. Oxidation air blower 5. Sorbent silo 6. Tank for freshly prepared scrubbing suspension 7. Gypsum slurry Hydrocyclone station 8. Vacuum belt filter 9. Vacuum pump 10. Waste water Hydrocyclone station 11. Circulating water tank |
Advantages
- High removal efficiency
- Low sorbent and power consumption
- High reliability and availability
- Stable byproduct (commercial grade gypsum)
Projects
- Dangjin Thermal Power Plant Units 1~4
500MWX 4, Korea (1995)
- Cheongju Local Heating Public Cooperation, Korea (2000)
- Samcheonpo Thermal Power Plant Units 1~4
560MW X 4, Korea (2002)
- Hadong Thermal Power Plant Units 7~8
500MW X 4, Korea (2006)










