Languages
Dry type ESP

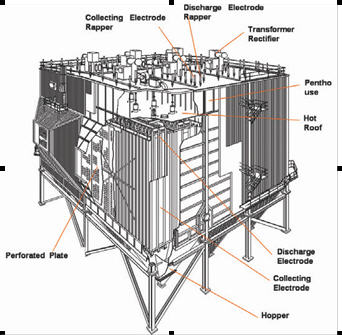
Electrostatic Precipitators (ESP)
Dry Type ESP
With an electrostatic precipitator (ESP), direct high voltage is applied to create a corona discharge to charge particles suspended in the gas and collect them through electrostatic attraction. An ESP is useful in removing particles in the sub-micron (0.1ß#) range which are difficult to capture with gravitational or centrifugal force.
Advantages
- Customized system design
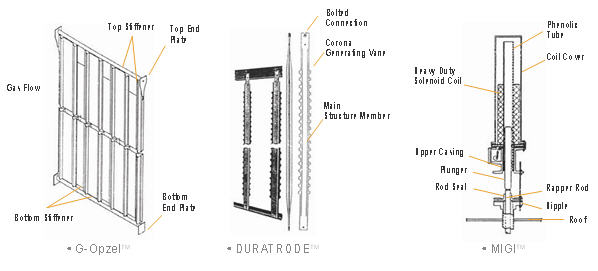
- Collection with G-OpzelTM Plate
- DURATRODETM discharge electrode
- MIGITM (Magnetic Impulse Gravity impact) rappers
- Semipulse and Multipulse for high collection and energy efficiency
Projects
- Boryeong Thermal Power Plant Units 1~8 500MW, Korea (1983~2006)
- Kasima Power Plant, Japan (2000)
- Taean Thermal Power Plant Units 7~8 500MW X 4, Korea (2004)
- Taichung Thermal Power Plant Units 9~10 550MW X 2, Taiwan (2001)
- Pohang Sintering Plants 1~4 (POSCO), Korea (1986~2008)
- Gwangyang Ferronickel Plant (POSCO), Korea (2007)








